How AI Predicts Ingredient Pairings
• Updated
AI is changing how we think about food by analyzing both chemical data and recipe history to find ingredient pairings that work. Here's how it works:
- Flavor Chemistry: AI studies the molecular makeup of ingredients, identifying shared aroma compounds (like linalool in strawberries and basil) or complementary profiles (e.g., acidic tomatoes balancing creamy cheese).
- Machine Learning: Systems like FlavorGraph use graph-based models and transformers to analyze vast recipe databases and flavor molecules, predicting pairings with high accuracy.
- Practical Tools: Apps like Honeydew Recipe Manager suggest recipes based on what you have, recommend substitutions, and even explain why certain combinations work.
AI doesn’t just stick to classic pairings - it discovers unexpected ones (e.g., white wine with condensed mushroom soup) and helps tailor recipes for dietary needs. This combination of science and data is making cooking smarter and more efficient.
The Science Behind AI Ingredient Pairing
Flavor Chemistry Basics
AI predicts ingredient pairings by diving deep into the chemical makeup of flavors. Every ingredient is packed with volatile compounds that shape its taste and aroma. Using tools like gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), AI systems identify and map these compounds, creating detailed chemical profiles. For instance, the Flavonomics platform has analyzed over 4,250 ingredients and explains why chocolate and coffee make such a great duo - they both contain roasted pyrazines, compounds that amplify each other's flavor.
To process this data, AI converts molecular structures into mathematical representations like SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System). It then evaluates factors like molecular weight, polarity, and charge to predict how these compounds interact with taste receptors. In July 2025, researchers unveiled the FART (Flavor Analysis and Recognition Transformer) model, which achieved over 91% accuracy in predicting sweet, bitter, sour, and umami tastes across 15,025 compounds.
"Taste perception originates from molecular interactions in the oral cavity between taste receptors and chemical tastants. Hence, the recognition of taste receptors and the subsequent perception of taste heavily rely on the physicochemical properties of food ingredients." - VirtuousMultiTaste Research Team, npj Science of Food
AI identifies pairings using two main strategies: chemical overlap and complementary profiles. Chemical overlap occurs when ingredients share key aroma compounds, like linalool, which is found in both strawberries and basil. Complementary profiles, on the other hand, balance contrasting elements for a harmonious result. FlavorDB has cataloged over 25,500 compounds, but only about 9% are linked to specific foods, leaving a vast amount of "dark matter" for AI to decode.
Machine Learning Methods for Ingredient Pairing
Beyond chemistry, AI taps into machine learning to uncover effective ingredient pairings. Graph-based models are a popular method, where ingredients and their chemical compounds are represented as nodes in a network. This approach helps reveal hidden relationships between seemingly unrelated flavors. A notable example is FlavorGraph, developed by Sony AI and Korea University in April 2021.
Meanwhile, transformer architectures, originally designed for processing language, are now being used to interpret chemical structures. The FART model, for instance, uses integrated gradients to pinpoint which atoms in a molecule contribute to specific tastes like "sweet" or "sour". Other machine learning techniques, like Random Forest and Gradient Boosting, excel at classifying flavor profiles based on molecular data. In March 2024, researchers at KU Leuven used Gradient Boosting to study 250 Belgian beers, identifying ethyl acetate as the top predictor of consumer preference, with an R² value of 0.67.
The practical application of these methods is evident in tools like the FlavorMiner algorithm. By combining Random Forest models with molecular fingerprints, FlavorMiner achieves an impressive average ROC AUC score of 0.88 when predicting seven key flavor categories: floral, fruity, sour, sweet, bitter, off-flavor, and nutty. These AI models build on centuries of culinary knowledge, enabling the discovery of new pairings that elevate meal planning to a whole new level.
AI Found Flavor Combinations That Shouldn't Work
How AI Processes Data to Predict Pairings
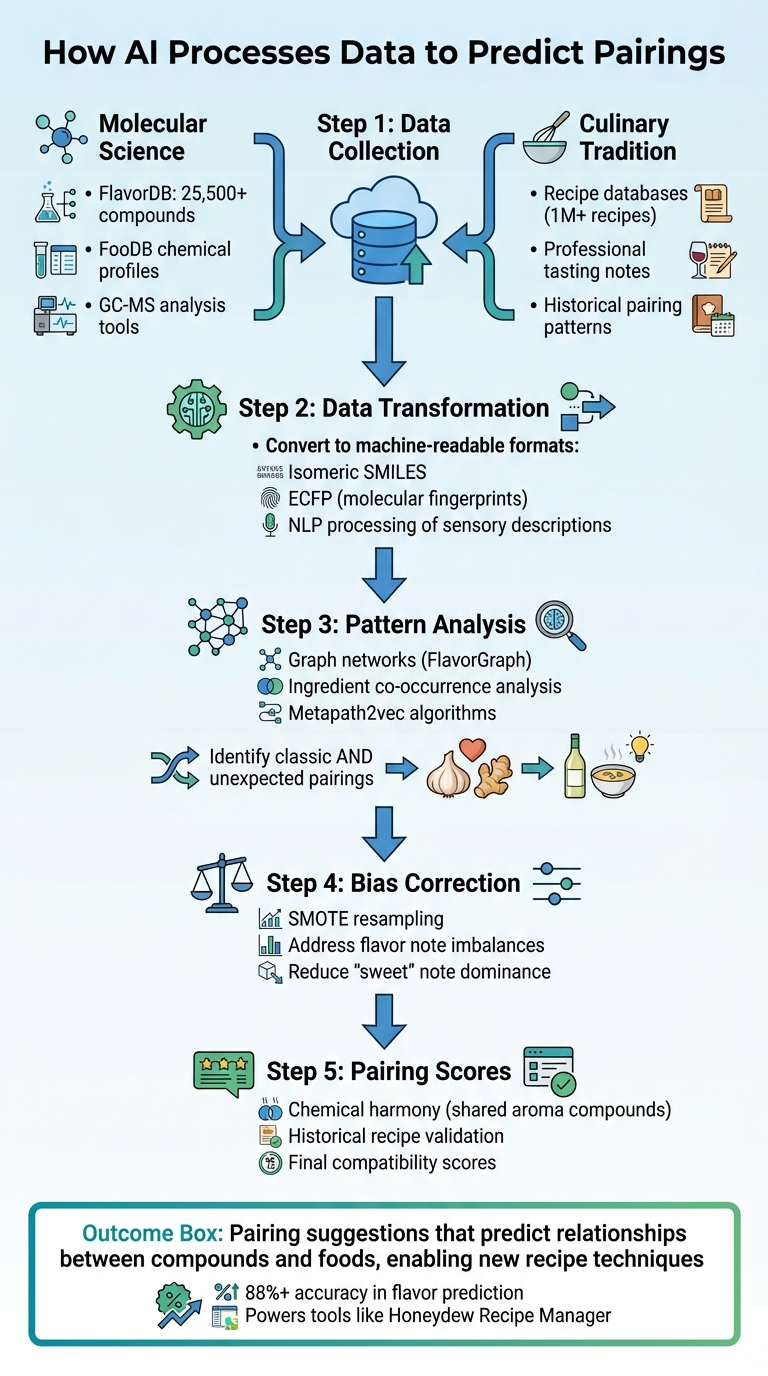
How AI Predicts Ingredient Pairings: From Data to Recipe Recommendations
Where AI Gets Its Training Data
AI leverages advanced machine learning techniques and taps into two primary data sources to predict ingredient pairings: molecular science and culinary tradition. On the molecular side, AI relies on chemical structure data from resources like FlavorDB, which catalogs over 25,500 compounds, and FooDB. These databases use tools such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to analyze volatile aroma compounds, creating detailed chemical profiles for ingredients.
On the culinary side, AI learns from vast recipe collections that document how ingredients have been paired historically. Systems like FlavorGraph combine these recipe databases with molecular data, blending chemical insights with real-world ingredient usage. Additionally, AI processes sensory descriptions from professional reviews and tasting notes using Natural Language Processing (NLP). This allows it to translate subjective terms like "earthy" or "citrusy" into structured, actionable data. Tools like FlavorMiner also contribute by analyzing validated flavor profiles to enhance pairing predictions.
The AI Data Processing Steps
AI transforms ingredient information into machine-readable formats, such as Isomeric SMILES or ECFP, which capture essential chemical properties. This enables algorithms to evaluate the compatibility or contrast between different ingredients.
Next, AI examines how often ingredients co-occur in recipes. By analyzing patterns - like which ingredients frequently appear together - AI uncovers relationships that go beyond chance. Systems such as FlavorGraph use graph networks, where foods and chemical compounds are represented as interconnected nodes. Techniques like metapath2vec help identify both classic pairings (e.g., garlic and ginger) and unexpected combinations (like white wine and condensed mushroom soup).
"The outcome is pairing suggestions that achieve better results than ever before. These suggestions can be used to predict relationships between compounds and foods, hinting at new and exciting recipe techniques." - Donghyeon Park, Korea University
AI also addresses imbalances in flavor note frequency - such as the dominance of "sweet" notes - by using resampling strategies like SMOTE to reduce bias. Finally, pairing scores are assigned based on a combination of chemical harmony (shared aroma compounds) and historical recipe validation (how often ingredients have been paired in the past).
This refined process allows tools like Honeydew Recipe Manager to deliver smarter, more personalized meal planning options.
AI Applications in Meal Planning and Cooking
AI-Powered Recipe Suggestions
AI has transformed the way we discover recipes, making meal planning more efficient and personalized. By analyzing flavor profiles, available ingredients, and individual preferences, AI eliminates the need for endless scrolling and guessing. Instead, it uses advanced culinary data and chemical analysis to craft harmonious ingredient combinations.
This process goes far beyond basic keyword matching. For instance, if you input ingredients like chicken, lemon, and garlic, the AI doesn't just suggest random recipes. It digs deeper, analyzing the molecular structures of these foods and comparing them against vast flavor databases. This allows it to recommend complementary additions - like specific herbs or spices - that share aroma compounds with your chosen ingredients. Tools like FlavorGraph excel at identifying both timeless and unexpected pairings that align with these chemical interactions.
For those with dietary restrictions, AI introduces even greater precision. Using constraint-based filtering, it ensures every recipe aligns with specific needs, whether it's Halal, Kosher, vegan, or gluten-free. The system even finds molecularly similar substitutes for restricted ingredients, preserving the dish's integrity.
"Substitution rarely has a one-to-one analogue and often requires compensatory adjustments to restore flavor, aroma, texture, emulsification, stability, and processing behavior." – Emel Oz and Fatih Oz, Ataturk University
AI handles these complex substitutions with ease, balancing multiple factors to replicate elements like dairy fat's creamy texture in vegan recipes. This technology powers practical tools like the Honeydew Recipe Manager, making these advanced capabilities accessible to everyday users.
Honeydew Recipe Manager: AI Features in Practice
Honeydew Recipe Manager takes these AI innovations and applies them directly to meal planning, simplifying the process for users. By leveraging flavor chemistry and machine learning, the app creates personalized weekly meal schedules based on your dietary preferences, nutritional goals, and what you already have on hand. With its Pantry Mode, you can even snap a photo of your refrigerator, and the AI will instantly recognize the ingredients and suggest recipes designed to reduce waste while enhancing flavor combinations.
One standout feature is its smart ingredient substitution. If you're missing a key ingredient, the AI doesn’t just leave you stranded - it identifies suitable replacements that maintain the dish's intended taste and texture. Honeydew also includes a photo-to-recipe function, where you can upload an image of a dish, and the AI generates a recipe complete with estimated ingredients and nutritional information.
For households juggling diverse dietary needs, the app simplifies grocery shopping by creating auto-generated lists organized by store sections and tailored to everyone's restrictions. On top of that, the AI cooking assistant offers real-time guidance, answering questions about techniques, timing, and adjustments. These features all rely on the same flavor chemistry principles that predict successful ingredient pairings, making meal preparation smoother and more enjoyable.
Conclusion
Main Points to Remember
AI is reshaping how we understand ingredient pairings by combining molecular science with recipe history. Systems like FlavorGraph - trained on a massive dataset of 1 million recipes and chemical profiles from over 1,500 flavor molecules - uncover both classic combinations and surprising matches that might escape human intuition. Using advanced machine learning techniques like Gradient Boosting and Random Forest, these systems excel at handling complex, non-linear flavor interactions, achieving accuracy rates of over 88% in predicting flavor categories.
For home cooks, this means smarter substitutions, personalized recipe ideas, and even optimized meal planning. Tools like Honeydew Recipe Manager showcase how AI blends science with tradition, bringing cutting-edge technology into everyday kitchens. As these advances continue, AI is poised to not only enhance flavor pairing but redefine the entire cooking experience.
What's Next for AI in Cooking
While today’s AI tools are already improving meal planning and ingredient selection, the future promises even more exciting developments. Next-generation AI will focus on balancing flavor, nutrition, texture, and sustainability. Emerging chemical language models could enable large-scale searches for new flavor compounds, much like how drug discovery works. AI is also expected to help identify plant-based alternatives that mimic the "mouthfeel" and stability of animal-based ingredients, addressing both health and environmental challenges.
Another key trend is explainable AI, which aims to provide transparency by helping chefs and home cooks understand the reasoning behind each recommendation. One early example of AI in action is McCormick & Company’s "ONE" product line, launched in mid-2019. This AI-enabled seasoning range was developed through a four-year partnership with IBM Research, marking a significant step toward bringing this technology into consumer kitchens. As these tools evolve, they’ll continue to complement traditional culinary methods, making cooking smarter, more efficient, and less wasteful.
FAQs
How does AI predict which ingredients pair well together?
AI dives deep into the world of flavor by analyzing the chemical compounds that give ingredients their distinct taste and aroma. Using tools like gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, it maps out the unique chemical makeup of each ingredient. By comparing these profiles, AI can uncover shared or complementary compounds - like linalool or esters - that often lead to well-balanced flavor pairings.
But it doesn’t stop at chemistry. AI also taps into vast recipe databases and considers user preferences to fine-tune its suggestions. This mix of science and data allows AI to recommend ingredient pairings that are both inventive and rooted in solid culinary knowledge.
How does AI predict which ingredients pair well together?
AI dives into the science of flavor pairing by examining the chemical makeup of ingredients and how they interact. Tools like FlavorGraph rely on machine learning to sift through huge datasets of flavor compounds and recipes. These models uncover patterns in ingredient combinations, often revealing pairings that might never cross a human chef's mind.
With this technology, AI can recommend flavor matches that are both inventive and grounded in science. Whether you're a professional chef or a home cook, this opens up exciting opportunities to experiment in the kitchen. Plus, AI can tailor suggestions to fit your personal tastes, making meal planning not only easier but also a lot more adventurous.
How does AI help predict ingredient pairings and personalize meal planning?
AI is transforming the way we approach meal planning by taking individual preferences, dietary restrictions, and nutritional goals into account. For example, tools like Honeydew Recipe Manager make use of AI to simplify the process. They can import recipes from social media, create grocery lists, suggest ingredient swaps, and even recommend dishes tailored to specific diets, such as keto or vegan.
Another fascinating application of AI lies in flavor chemistry. By analyzing aroma compounds and culinary traditions, AI can predict ingredient pairings that complement each other beautifully. It goes a step further by aligning these suggestions with your personal tastes, ensuring the meals you prepare are not just healthy but also packed with flavor. This makes cooking a highly personalized and enjoyable experience for everyone.
